BIOLOGY(cells:an overview)
Just like the basic building block of all matter is an atom,cell is the basic building block of an organism.
Take for example a office as a cell all the employees of the office does the work similarly all the organelles of the cell perform activities.
Topics covered-
1.Microbiology and microscope
2.The cell theory
3.Types of cells
4.The components of a cell(organelles)
5.Brief explanation of each component of a cell
So the beginning of what we call the microbiology was from the microscope. It would be a little annoying if I tell you about the history of it but, believe me, it's super interesting.
 (source:internet)
(source:internet)
Microbiology and microscope -
-
So, literally, microscope was a really trendy product for the scientists in the times of the 16th century and there were many who made it by themselves.It is stated that the person named Anton Von Leeuwenhoek was the father of microbiology that is because he first observed the animalcules, what we call cell today.It would be hard to believe that he was a cloth seller and he,on purpose made his own microscope to look at the cloth,it was not very scientific action until he saw the pond water under the microscope and he got to see some really small creatures called microorganisms,and so began the world of microbiology.
The cell theory -
-
~All living things are made up of cells
~New cells are formed form preexisting cells
~the way an organism function depends on the way the cell works
Types of cells ⊙ -
In this blog we would be focusing more on the eukaryotic cells as they are more complex and have more features than the prokaryotic cell.
The components of a cell -
1.Nucleus
2.Endoplasmic Retticulum
3.Golgi apparatus
4.mitochondria
5.Lysosomes
6.Vacuoles
7. Plastids
8.Structure giving components
Below given is an animated view of cells
 (source:internet)
(source:internet)Below given is a real photograph of a eukaryotic cell under an electron microscope
Brief explanation of the components of a cell-
NUCLEUS(plural:nuclei)~
~small spherical body
~it is the control center of the cell
~it directs the growth of the cell and controls all the activities that are taking place in the cell
~it can be compared to the brain in human body as both perform same role i.e.,to control
~it contains the genetic material of the cell i.e.,DNA and genes
 (source:internet)
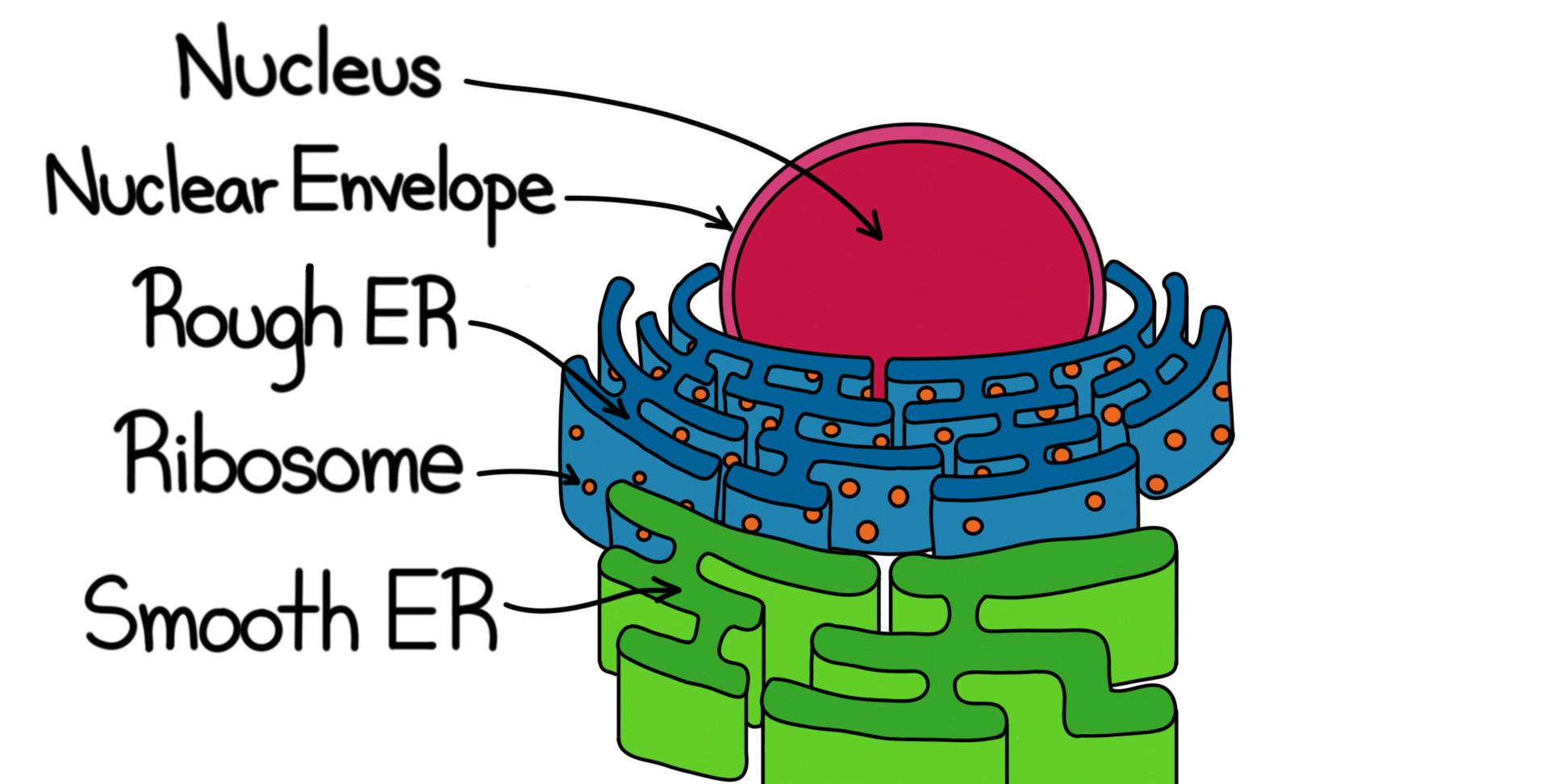
(source:internet)ENDOPLASMIC RETTICULUM(ER)-
~has large network of tubes and sheets
~there are two types of ER
1.Rough ER(RER)
2.Smooth ER(SER)
~the RER has ribosomes attached to it
~ribosomes are the protein manufacturers of the cell
~the SER manufacture lipids
~lipids are fat molecules
 (source:internet)
(source:internet)GOLGI APPARATUS(also called golgi body)-
~it contains membrane bound vessicles
~it functions are
~storage
~modification
~and packaging of products in vesicles
~and etc...
 (source:internet)
(source:internet)MITCHOCHONDRIA-
~it provides power to the cell to perform activities
~produces ATP molecules
~ATP molecules are Adenosine Triphosphate,it is the energy currency
of the cell
 (source:internet)
(source:internet)LYSOSOMES-
~contains digestive enzimes which helps the cell to digest its food
~they are waste disposal system of the cell
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/lysosome-56a27cb35f9b58b7d0cb394c.jpg) (source:internet)
(source:internet)VACUOLES-
~they are the storage sacs
~they are huge in plant cells
~they mostly contain some solid or liquid material stored in it
PLASTIDS-
~are found in the plant cell
~there are two tpes of plastids
1.chromoplasts
2.leucoplasts
~chromoplasts have pigments which give colour to them chlorophyll
~leucoplasts are colourless
STRUCTURE GIVING COMPONENTS-
~following give structure to the cell
1.Plasma membrane(give an outer covering to the cell so that the inner components do not spill out)
2.Cell wall(it is only found in plant cells and are an additional protective layer to the cell membrane)
3.Cytoskeleton(performs as a skeletal structure for the cell)
4.Cytoplasm(its a jelly like component of the cell in which all the organelles float)
~THE END~


I hope the blog is helpful,if there are some questions or doubts you can ask me here in the comment section :)
ReplyDeleteIt was helpful,thanks!
Delete